
Use PS1('> ') to change the promt to >ĭisp(a) will display the variable a. It is possible to change octave's prompt. The following commands can be used within octave: It is also possible to use if-conditions % i = 10 You have to be in the same dir as the file or add it to your search-path ( addpath()).įor- and while-loops are easy and useful in octave. % is also possible to return multiple valuesĬall your function in octave like function_name(5). The syntax is quite simple: function y = function_name(x)
#Gnu octave size windows
Subplot(x,y,POS) plot multiple graphs in one windows as a X-by-Y grid at position POS > subplot(1,2,1) įunctions are saved in files with the file-ending.
For other format see help plotįigure(1) plot(x, y) plot graph as figure 1 figure(2) plot(x, y2) plot graph as figure 2 Print -dpng 'myPlot.png' export plot as PNG file. Xlabel('Zoidberg'), ylabel('Bender'), legend('fry', 'lila'), title('Futurama') Example axis()Ĭolorbar display colorbar, kind of legendĮxample: imagesc(A), colorbar, colormap gray Labels Plot(x, y2, 'r') will plot a graph in red.Īxis() X-axis will start at a and goes to b, and Y-axis will start from c and goes to d. Hold on will plot updated in the current plot instead of replace the current plot. Plot(x, y) plot a graph with x as x-axis and y as y-axis. There exists serveral ways to create a inverse matrix in octave > inv(M) % warning: yes > sum(sum(M.* flipud(eye(4) ))) % sum of diagonal bottom left to top right > sum(sum(M.*eye(4))) % sum of diagonal top left to bottom right Let's check the sum of diagonals > M = magic(4) Hint: useful in combination with the identity matrix flipud(eye(4)) Sum of diagonals in a square matrixĮxample: A magic matrix is a square matrix where the sum of rows, columns and diagonals are the same result. You can search thru matrices and vectors with a condition > find(A > flipud(A) To find the largest value in a matrix you can either chain to max() functions or take the complete matrix. Max values and find() > max(magic(4)) % returns a 1x4 vector with max-values per column % in this case it doesn't matter if comma or semicolon is usedĬoncatenating Matrices > B = Output last element in Matrix > A(end, end)ĭisplay Data % show number in first row and second columnĪssign new Data % replace second column by 10, 11, and 12 Instead of typing a semicolon it is also possible to hit enter. The semicolon indicates a new row and a space or comma is a new column. The file will be saved in the current directory and will be loaded from the current dir. Save filename.txt v -ascii % save data of v in readable version To save a specific variable v to the file filename.dat save filename.dat v % save data of v in binary format You can save and load data in octave easily with the two commands save and load. Whos Provide detailed information on currently defined variables.Ĭlear will clear all variables or only the ones who are named. Who Lists currently defined varibales matchin the given pattern. For Matrix objects, the length is the number of rows or columns, whichever is greater (this odd definition is used for compatibility with MATHLAB). Length(A) Return the length of the object A. Size(A ) Return the number of rows and colums of A. y is the number of buckets.Įye(x ]) Produces an identity matrix. Hist(x ) Produce histogram counts of plots. The arguments are handled the same as the arguments for rand. Randn(x ) Return a matrix with normally distributed random elements having zero mean and variance one. Rand(x ) Return a matrix with random elements uniformly distributed on the interval (0, 1). Zeros(x ) behaves the same as ones() but will give a zero-matrix.

If y is provides it has the size x cross y. If only x is provided it is a squared matrix of size x. Help _function name_ will give you the man page of this function. Beware that ocatve is 1 based.ĭisplaying a range of numbers use v(3:5) to display the 3rd, 4th, and 5th number.
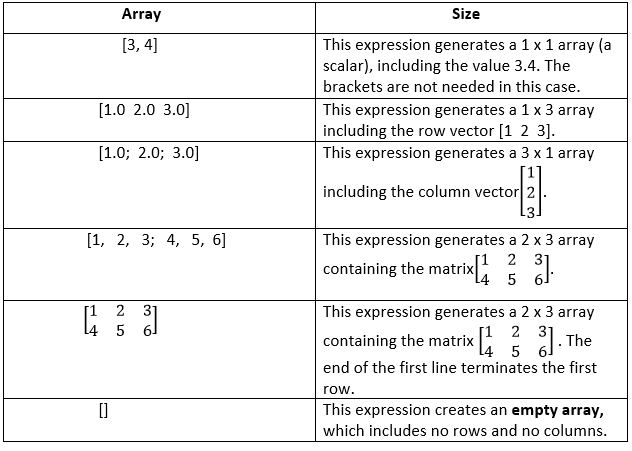
To display the 5th number of this vectors use v(5). V = 1:0.1:2 also creates a vector but with the numbers from one to two with a step size of 0.1. V = 1:5 creates a 1x5 Matrix (linear vector) with the numbers one to five. Hint: I also mad an octave docset for Dash: BasicsĪ semicolon at the end of a line will suppress the output GNU Octave is a high-level interpreted language, primarily intended for numerical computations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
